I just took the new CASP+ CAS-004 Exam on March 14. This exam is an unscored pass/fail exam. I passed. There were very many questions where the feeling was “when did we ever learn about this.” I’m an instructor for this course, and several others. So the moral of the story, let go of your negative feelings of uncertainty and failure. You ARE prepared, even if the subjects in the questions seem unfamiliar. Read the scenario, read the question, pick an answer. Go with your first answer. Don’t overthink it, and don’t second guess yourself. Never ever change an answer, the first impression is the good answer almost always.
This post is an accumulation over time, and I am adding new content as it happens. Also, check me out on Reddit. https://www.reddit.com/r/CompTIA/comments/te8i8y/i_just_passed_the_casp_cas004_exam/
[Bob says: As of July 13 2022 there is more information on the Linux Forensics Simulation and also the usual Question1 PBQ. Read all the way to the end, and check the comments for deeper insights. The newest bits are at the bottom.]
There was only one Performance-Based-Question (PBQ) and it was the first one on the exam. The one I had was a Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery scenario. There was a network map of two offices connected by a VPN, and a number of different hosts at each location. In the scenario, there was a disaster at Location A. There were three “findings” about certain situations that weren’t working correctly, and I had to match each finding to one or more devices. One of the findings also required I choose a mitigation from a drop-down list. I did not think this was overly hard, although I did reset the board 3 times before settling on my 4th answer set. Usually I wait to do the PBQs at the end, but this one seemed simple enough so I just completed PBQ1 and moved on.
Then there was a “Virtual Environment” question. These are different, I have not seen one like this. You HAVE to answer it in the order you get it, if you skip it you can’t go back. and you get no points. Once you have answered it, you can’t go back either. My Virtual question gave me a simulated Linux Ubuntu desktop. The scenario was that this system was maliciously breached, and had been repaired, but there is concern by the security tech that there is a malicious TCP process still running, and your job it to find it, identity it, disable it, and kill it. All in the constrains of the Ubuntu terminal window. You definitely need to know your Linux commands for this one. This is similar to the PBQ 1-3 listed below
To get good practice in Linux, I would recommend installing Kali Linux as a virtual machine, and learning how to work at the terminal window.
There was a lot of emphasis on Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery, Cloud, Authentication, and Software Security.
If you have taken this exam recently and wish to contribute some of your experiences, I would add them to this article.
Here are some tips on the Performance Based Questions (PBQ) from the CAS-003. They may be out of date, but in my experience these PBQ questions hang around for a while. These come from Quizlet. https://quizlet.com/it/513316332/casp-cas-003-performance-based-questions-flash-cards/ These are offered as examples, not verbatim copies of actual exam questions.
PBQ 1 Part 1 As a security administrator, you are asked to harden a server running Red Hat Enterprise Server 5.5 64-bit. This server is being used as a DNS and time server. It is not used as a database, web server, or print server. There are no wireless connections to the server and it does not need to print. You need to disable and turn off unrelated services and processes. What command would you use to check the configuration
PBQ 1Part 2 As a security administrator, you are asked to harden a server running Red Hat Enterprise Server 5.5 64-bit. This server is being used as a DNS and time server. It is not used as a database, web server, or print server. There are no wireless connections to the server and it does not need to print. You need to disable and turn off unrelated services and processes. What services would you need to disable to accomplish this
httpd
mysqld
lpd
bluetooth
wpa supplicant
PBQ 1 Part 3 As a security administrator, you are asked to harden a server running Red Hat Enterprise Server 5.5 64-bit. This server is being used as a DNS and time server. It is not used as a database, web server, or print server. There are no wireless connections to the server and it does not need to print. You need to disable and turn off unrelated services and processes. After you have stopped the service using the service “service” stop command, what needs to be done?
Out of the six downloads, some may be http and others https. Use only the Https
the file does not download in a reasonable amount of time or you get a certificate warning
A new PBQ submitted on March 31, 2023
I was given two snippets of code (both were python if I remember right) and had to identify the vulnerability in each, as well as how to remediate it. Being able to identify and remediate injection attacks, insecure object references, and other issues in the OWASP top 10 should be enough.
And some more on this “code security” PBQ.
…the old code snippet sim from CAS003 that you can find here https://www.examtopics.com/discussions/comptia/view/62960-exam-cas-003-topic-1-question-480-discussion/
Check out this chat of mine on Reddit – https://www.reddit.com/r/CompTIA/comments/te8i8y/i_just_passed_the_casp_cas004_exam/
Added on 2022-06-28 – Searching YouTube using CAS-004 Forensic Linux Sim I did find a two hour video tutorial on Linux Forensics at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTEj8UY2TA8. I am watching it now. Some of this content may be useful in understanding the process that is being tested in the Sim.
Question from a test taker about the Simulated Virtual Environment question
I have to be careful here, I can provide guidance but not explicit information. Conversation follows.
M – We were just talking on Reddit. I remember the exercise almost verbatim but I don’t want to make you feel uncomfortable with non-disclosure etc. But if you have any insight or tools to help me learn command line quickly or what to look for I think I can pass the rest. I’m fairly certain the exercise is what held me back. Let me know and I can send it to you. Also looking forward to reading your blog tomorrow.
Bob – Ok so you have some work ahead of you but not a lot. You need a few Linux command line tools
First step is to get a copy of Linux on a computer. Easiest way is to set up a virtual machine. I have a VM of Kali Linux I use for all sorts of security work. But Ubuntu would be the distro on the test. Ever set up a VM?
I use Virtual Box. It is free. Got to virtualbox.org. Download and install. After that install the Extension Pack
Then go to Kali.org or ubuntu.com. I know Kali better. But they are both Debian Linux distros. In Kali, choose the Virtual Machine option, and then download the VirtualBox option. Save it where you can find it, then open Virtual Box and go to File, Import Appliance, and then find your download and you are done.
Let me know if you get it working. Or let me know if you already have done this.
M- Thank you for sending, tried to download Kali but I don’t have enough space on my computer its just a basic acer. trying to find a better option
Bob- Ah too bad. You could make a bootable USB drive to get around that problem, look lower on the Kali downloads page. Unfortunately you can’t flip back and forth between the windows host OS and the Kali virtual OS. You boot into the drive and its all Kali all the time.
I’ll send you a list of commands to learn, just need some time to pull them together.
Here are some Linux Command to learn Linux Commands
At the beginning of the question the test offers suggestions about what Linux commands may be useful in this question. Take the hint. Write the commands on your note card. You will be using them.
If you need help try the man command. For instance, man netstat shows available commands in netstat.. Press q to quit or exit. Generally speaking Windows help or Linux man information is available in the testing environment. Not sure? Get help!
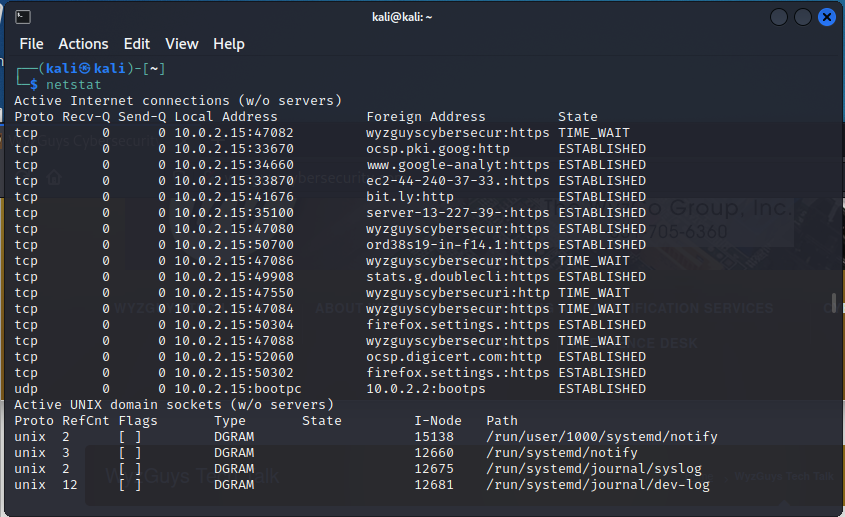
One command you might need for this question is netstat This will show a running list of TCP connections. I opened my website at http://wyzguyscybersecurity.com. It shows up on the first line in the image below.
You can see all the other TCP connections. You will have to scroll back to the top of this report, as it goes on for several pages.
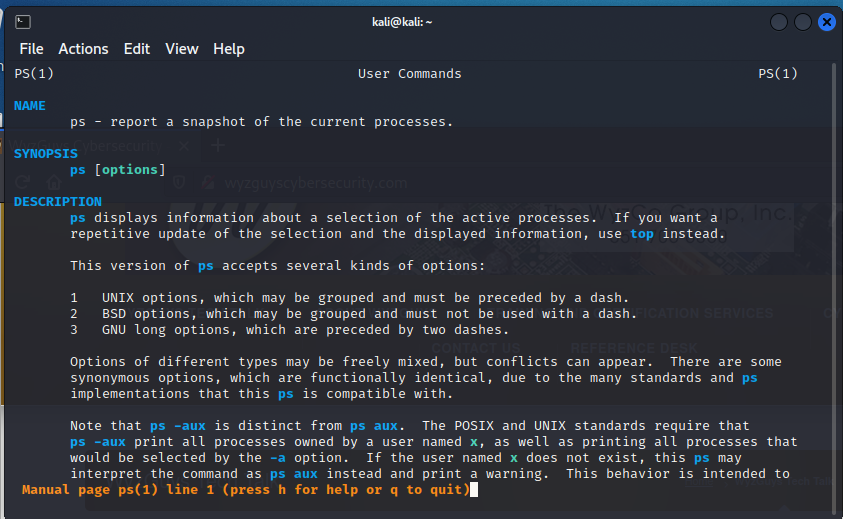
Another command you may need is ps. This will show you the process IDs for all running processes. Try to find the rogue process in question. Here is the man page.
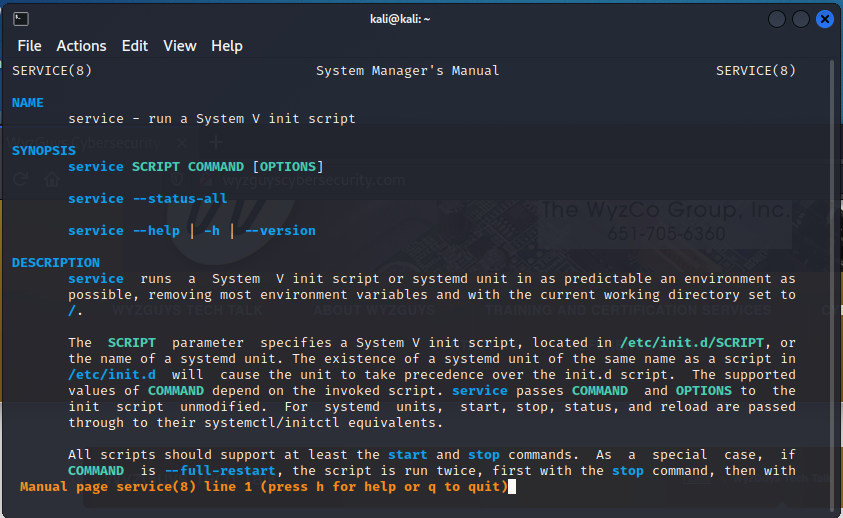
Here’s the man page for the service command
Let’s try the command service –status-all. You should see a list of running services. If we were trying to stop a rouge service named rogue type service rogue stop
The kill command will kill the rogue service. Do so by command kill -9 262 (example) where 262 is the id number associated with the service. Of course you will use the process ID you identified earlier.
This question will take a lot of time in the middle of the exam, but it is a must do with no backs. So practice makes perfect here. Find your way by practicing on the Kali Linux VM you created earlier.
2022-07-12
One of the test takers I am talking with has failed the CAS-004 a total of four times now. He is thinking that it Sim is causing him to fail, but I think he has the Sim process pretty well figured out, and I suggested that he might be only a few points from passing, and that his missing point may lie elsewhere in the test. No guarantees on this solution, this is just what he is doing. The email string between us follows below:
TESTER: FYI, I have had the same sim question every time, all 4.
The Linux question has two parts, first you have a rogue tcp process and second you need to find a keep a malicious service (called malicious.service) from restarting.
The steps I took were as follows:
- netstat -nalp to find the tcp process, there was only one established process like port 50200 to 1337,
- lsof -i :50200, found the pid which was something like 2430
- kill -9 2430
- used systemctl to find the malicious.service
- systemctl stop malicious.service
- systemctl disable malicious.service
- I did find the malicious.service in /etc/systemd/system and deleted it with elevated privileges
- I rebooted twice and the tcp process or the malicious service never came back.
I figured that I answered the questions correctly and the service never came back.
In talking with a guy that I work with that knows linux much better than I do, he said that maybe the question is not written great and you need to do more.
He suggested before I kill the tcp process that I find out the location of the exe. Possibly in usr/bin or somewhere else and then kill the process and remove the exe before I stop and disable the malicious.service? He said that deleting the malicious.service that I found in the etc/systemd/system probably isn’t what was necessary to pass the test?
My response:
That process looks pretty solid to me. I like your colleague’s suggestion, so I would try that next time.
From the feedback I have been getting, it seems there is a malicious file to find and remove. Presumably named whatever the process was named. I think there is a list command (ls) that search iteratively through the nested file structure that uses the ../../../ filename structure. Type the ls .. command to list the contents of the parent directory one level above. Use ls ../.. for contents two levels above: See the article on the ls command at https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/the-linux-ls-command-how-to-list-files-in-a-directory-with-options
I believe that the sim is not all or nothing type scoring, that you get partial credit for getting most of the process right. I could be wrong, but I believe that is the case with the standard PBQs, too.
There is a possibility you are missing points in the multiple choice questions. Since this is Pass/Fail, you may be very close to a pass, and just need one or two more answers. Pay close attention to questions that have more than one correct answer, make sure you choose the answer that is “BEST” in relation to the scenario and the question. For example, there is a scenario, a question, and three of the four answers are correct from a certain perspective. Make sure the answer you choose is the most specific for the question. If there is a n answer that is generally correct, and an answer that is specifically correct, choose wisely. Often the most specific solution is the best one.
Are you taking this test as a home proctored exam? I have heard horror stories galore about overzealous proctors invalidating your test results. If this applies to you, go to a testing center next time
2022-07-13
CAS-004 PBQ Solution
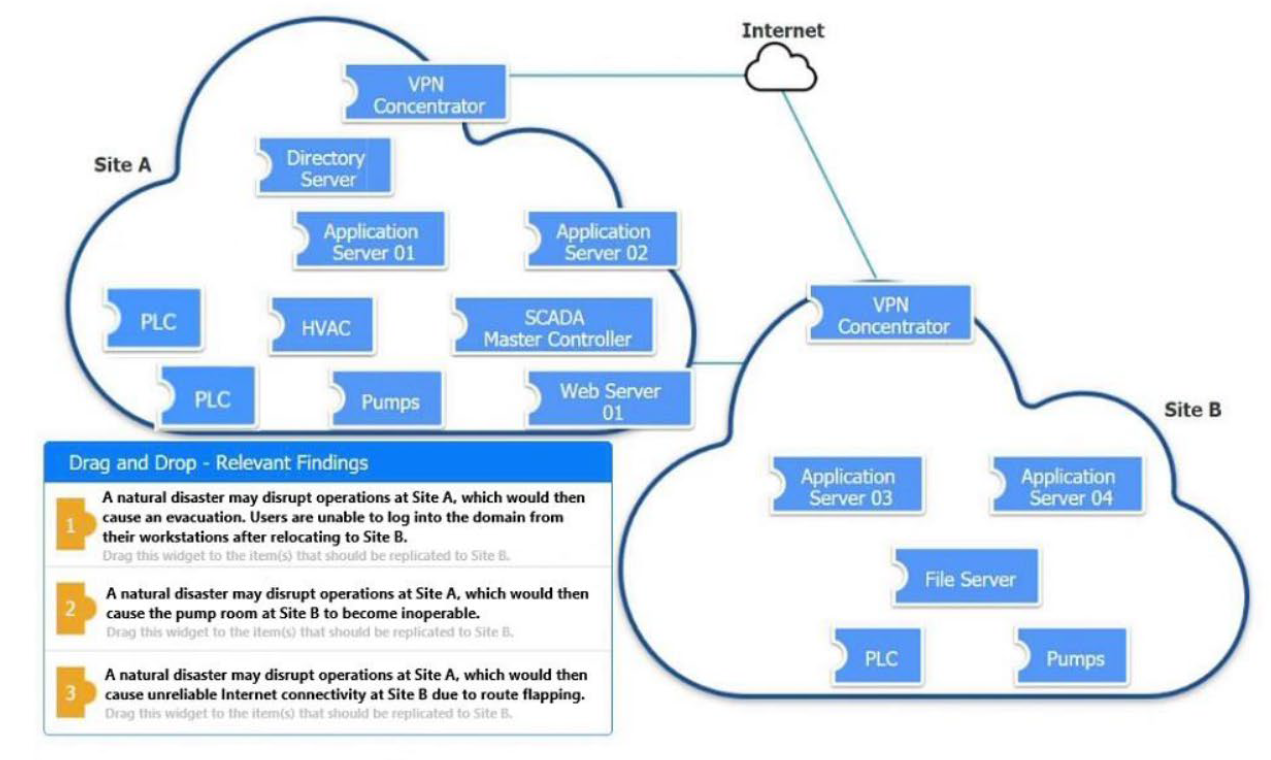
A contributor provided this solution for the PBQ that is usually Question 1 on the exam. This is NOT the dreaded Linux Simulation, just the standard PBQ. Never the less, from a scoring stand point this is important. If you are failing, you may be missing THIS question, and doing fine on the Sim. You can skip and return to finish it later but now you may not need to. These images are from a practice exam source, not my own. Again, I am just curating information that can be found on the web or on commercial test prep resources.
Click on the images to make them bigger.
The Question
The Answer
The contributor dug a little deeper on the web and found another answer for the drag and drop. The directory server is #1, the SCADA master controller is #2 and the VPN concentrator is #3.
Bob says – I removed the Answer image since the information on the illustration was incorrect. The answers given were #1 VPN Concentrator (wrong), #2 Pumps (wrong), #3 Directory Server (wrong). If you are using this practice test, please do not rely on the answers shown. The practice test is from Exam-Labs
Another contributor adds: For the PBQ, with the wrong selections from before, there was another step. After dragging the 3 selections, you also had to click on Directory Server, and choose from a drop down list of 8-9 choices of WHAT you were doing with that directory server.
Share
MAR





About the Author:
I am a cybersecurity and IT instructor, cybersecurity analyst, pen-tester, trainer, and speaker. I am an owner of the WyzCo Group Inc. In addition to consulting on security products and services, I also conduct security audits, compliance audits, vulnerability assessments and penetration tests. I also teach Cybersecurity Awareness Training classes. I work as an information technology and cybersecurity instructor for several training and certification organizations. I have worked in corporate, military, government, and workforce development training environments I am a frequent speaker at professional conferences such as the Minnesota Bloggers Conference, Secure360 Security Conference in 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, the (ISC)2 World Congress 2016, and the ISSA International Conference 2017, and many local community organizations, including Chambers of Commerce, SCORE, and several school districts. I have been blogging on cybersecurity since 2006 at http://wyzguyscybersecurity.com