 A quick Saturday digest of cybersecurity news articles from other sources.
A quick Saturday digest of cybersecurity news articles from other sources.
Fake Trump Sex Tape Lure Delivers QRat
While reviewing spam traps, a particular campaign piqued Trustwave’s interest primarily because the attachment to the email did not coincide with the theme of the email body. The email, with the Subject “GOOD LOAN OFFER!!”, at first glance, looks like the usual investment scam. No obfuscation in the email headers or body is found. Interestingly, attached to the email is an archive containing a Java Archive (JAR) file called “TRUMP_SEX_SCANDAL_VIDEO.jar”. The file is the QNODE DOWNLOADER, which is one of QRat’s downloaders.
MS-ISAC Releases Cybersecurity Advisory on Zyxel Firewalls and AP Controllers
Original release date: January 8, 2021
The Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) has released an advisory on a vulnerability in Zyxel firewalls and AP controllers. A remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability to take control of an affected system.
Backdoor account discovered in more than 100,000 Zyxel firewalls, VPN gateways
The username and password (zyfwp/PrOw!aN_fXp) were visible in one of the Zyxel firmware binaries. Update firmware now!
REFERENCES:
Zyxel: https://www.zyxel.com/support/CVE-2020-29583.shtml
EYE: https://www.eyecontrol.nl/blog/undocumented-user-account-in-zyxel-products.html
CVE: https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-29583
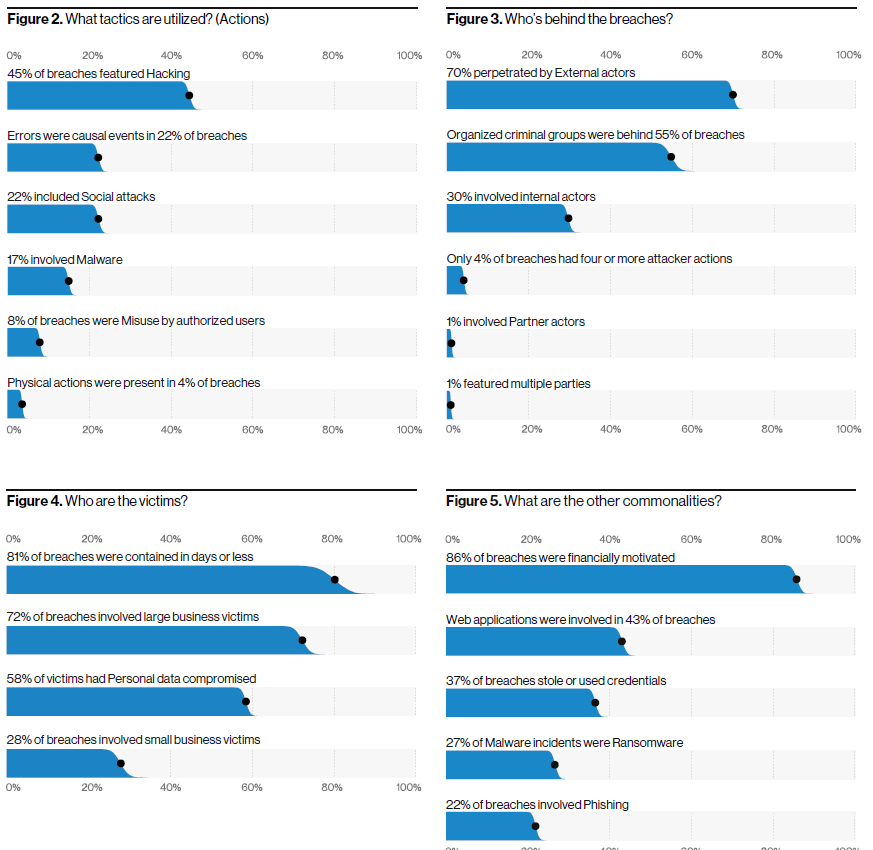
Verizon 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report
Download the PDF.
It’s Sad We Need to Say This But Beware of Puppy Scams. No, Really.
From KnowBe4 CyberHeist News. Researchers at Anomali have discovered eighteen scam websites offering pets for sale. Most of the websites purport to be selling dogs, although some offer cats and birds as well. The sites are all operated by the same group of scammers that use similar social engineering tactics to lure people in.
“The websites all share similar and sometimes identical text in their reviews/testimonials pages,” the researchers write. “There are also numerous typos in the testimonials with one post discussing how a German Shepherd had ‘hatched’ and was available, which is a clear copy-and-paste error from the actors’ bird fraud websites.”
While the scammers’ writing skills won’t win any awards, the photos of puppies may be enough to get people to lower their defenses. If a user clicks the “Buy me!” button, they’ll be taken to a contact form where they can get in touch with the scammers.
The researchers explain that the scammers are exploiting the holiday season as well as the increased demand for pets amid the pandemic.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has increased pet purchases as stay-at-home policies and remote work makes people seek companionship from their animal friends, a condition that may amplify the bad actors’ ability to run a more successful scam,” the researchers write.
“Furthermore, these scams focus on purebred dogs, which again are increasingly difficult to find.” Anomali offers the following tips for users to avoid falling for scams:
- “Be extremely cautious if the price is too good to be true.
- “Be extremely cautious if the site does not provide you with the owner’s names, address, and social pages.
- “Pay attention to elaborate testimonials that are too good to be true. They are often copied too, so you may google a part of it to see if it is unique.
- “Pay attention to typos and phrases like “Labrador baby had hatched,” scammers often sloppy in their templates and have bad English.
- “If they give you a phone number, try Googling it. Often the fraudsters use the same phone number for different schemes, and it might be already listed on some scam lists.
- “Be extremely careful if you are advised to pay for your future pet with Bitcoins or gift cards, which is even more suspicious.”
NSA Releases Guidance on Eliminating Obsolete TLS Protocol Configurations
Original release date: January 5, 2021
The National Security Agency (NSA) has released a Cybersecurity Information (CSI) sheet on eliminating obsolete Transport Layer Security (TLS) configurations. The information sheet identifies strategies to detect obsolete cipher suites and key exchange mechanisms, discusses recommended TLS configurations, and provides remediation recommendations for organizations using obsolete TLS configurations.
CISA encourages administrators and users to review NSA’s CSI sheet on Eliminating Obsolete TLS Protocol Configurations for more information.
CISA Updates Emergency Directive 21-01 Supplemental Guidance and Activity Alert on SolarWinds Orion Compromise
Original release date: January 6, 2021
CISA has released Emergency Directive (ED) 21-01 Supplemental Guidance version 3: Mitigate SolarWinds Orion Code Compromise, providing guidance that supersedes Required Action 4 of ED 21-01 and Supplemental Guidance versions 1 and 2.
- Federal agencies without evidence of adversary follow-on activity on their networks that accept the risk of running SolarWinds Orion in their enterprises should rebuild or upgrade, in compliance with hardening steps outlined in the Supplemental Guidance, to at least SolarWinds Orion Platform version 2020.2.1 HF2. The National Security Agency (NSA) examined this version and verified it eliminates the previously identified malicious code. This version also includes updates to fix un-related vulnerabilities, including vulnerabilities that SolarWinds has publicly disclosed.
- Federal agencies with evidence of follow-on threat actor activity on their networks should keep their affected versions disconnected, conduct forensic analysis, and consult with CISA before rebuilding or reimaging affected platforms and host operating systems.
The updated supplemental guidance also includes forensic analysis and reporting requirements.
CISA has also updated AA20-352A: Advanced Persistent Threat Compromise of Government Agencies, Critical Infrastructure, and Private Sector Organizations, originally released December 17, 2020. This update includes new information on initial access vectors, updated mitigation recommendations, and new indicators of compromise (IOCs).
Share
JAN



About the Author:
I am a cybersecurity and IT instructor, cybersecurity analyst, pen-tester, trainer, and speaker. I am an owner of the WyzCo Group Inc. In addition to consulting on security products and services, I also conduct security audits, compliance audits, vulnerability assessments and penetration tests. I also teach Cybersecurity Awareness Training classes. I work as an information technology and cybersecurity instructor for several training and certification organizations. I have worked in corporate, military, government, and workforce development training environments I am a frequent speaker at professional conferences such as the Minnesota Bloggers Conference, Secure360 Security Conference in 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, the (ISC)2 World Congress 2016, and the ISSA International Conference 2017, and many local community organizations, including Chambers of Commerce, SCORE, and several school districts. I have been blogging on cybersecurity since 2006 at http://wyzguyscybersecurity.com