Computer and Network Reference
The following information is provided as a free informational service on a variety of Information Technology subjects. Click on the subject heading below to expand list of subject matter.
- Computing and Networking
- Microsoft
- Cisco
- TCP/IP Networking
Start a continuous PING command
Start->Run->CMD->enter
ping 192.168.1.254 –t (ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -t)
Comparison of the OSI and DOD models
| DOD Model | OSI Model | Network Protocols | |
| Process / Application | Application | Telnet, FTP, SMTP, FTAM (File Transfer, Access, and Management), VTP (Virtual Terminal Protocol),CMID (Common Management and Information Protocol | |
| Presentation | ASCII, EBCDIC, JPEG, GIF, TIFF, MPEG, WAV | ||
| Session | RPC, ZIP (Zone Information Protocol), SCP (Session Control Protocol) | ||
| Host to Host | Transport | TCP, UDP, SPX, NBP (Name Binding Protocol) | |
| Internet | Network | IP, ICMP, IGRP, IPv6, GRE, IPX in IP, L2TP, ARP, RARP, Ping, Tracert, IPX, BGP, OSPF, RIP | |
| Network Access | Datalink | Logical Link Control (LLC)Layer | LAN – Ethernet (802.3), Fast Ethernet, Token Ring (802.5), Wi-Fi (802.11), FDDI |
| WAN -Frame Relay, ATM, LAP, LAPB (Link Access Procedure, Balanced), SDLC(Synchronous Data Link Control), PPP, SMDS, SIP | |||
| Media Access Control (MAC) Layer | MAC (hardware) addressing | ||
| Physical | Electrical (Copper), Optical (Fiber), Radio (Air), Photonic (Light, Laser) |
back to top
Memory Chart
| Type | Speed | Bus Speed | |
| DDR | PC2100 | 266Mhz | 133MHz |
| DDR | PC2700 | 333MHz | 166MHz |
| DDR | PC3200 | 400MHz | 200MHz |
| DDR | PC3500 | 433MHz | 216MHz |
| DDR | PC3700 | 466MHz | 233MHz |
| DDR | PC4000 | 500MHz | 250MHz |
| DDR | PC4200 | 533MHz | 266MHz |
| DDR | PC4400 | 550MHz | 275MHz |
| DDR | PC4500 | 566MHz | 283MHz |
| DDR | PC4800 | 600MHz | 300MHz |
| DDR | PC5000 | 625MHz | 313MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-4200 | 533MHz | 266MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-5400 | 667MHz | 333MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-6000 | 750MHz | 375MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-6400 | 800MHz | 400MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-8000 | 1000MHz | 500MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-8800 | 1100MHz | 550MHz |
| DDR2 | PC2-9000 | 1120MHz | 560MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-6400 | 800MHz | 400MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-8500 | 1066MHz | 533MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-10666 | 1333MHz | 667MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-12800 | 1600MHz | 800MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-14400 | 1800MHz | 900MHz |
| DDR3 | PC3-16000 | 2000MHz | 1000MHz |
IEEE 802 Working Groups and Networking Protocols
| Standard | Name | Description | Status |
| 802.1 | Higher Layer LAN Protocols Working Group | Active | |
| 802.2 | Novell | Logical Link Control Working Group | Inactive |
| 802.3 | Ethernet | Ethernet Working Group | Active |
| 802.4 | Token Bus Working Group | Inactive | |
| 802.5 | Token Ring | Token Ring Working Group | Inactive |
| 802.6 | Metropolitan Area Network Working Group | Disbanded | |
| 802.7 | Broadband TAG | Disbanded | |
| 802.8 | Fiber Optic TAG | Disbanded | |
| 802.9 | Isochronous LAN Working Group | Inactive | |
| 802.10 | Security Working Group | Inactive | |
| 802.11 | Wi-Fi | Wireless LAN Working Group | Active |
| 802.12 | Demand Priority Working Group | Inactive | |
| 802.14 | Cable Modem Working Group (Temporarily housed off-site) | Disbanded | |
| 802.15 | Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Working Group | Active | |
| 802.16 | Broadband Wireless Access Working Group | Active | |
| 802.17 | Resilient Packet Ring Working Group | Active | |
| 802.18 | Radio Regulatory TAG | Active | |
| 802.19 | Coexistence TAG | Active | |
| 802.20 | Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) Working Group | Active |
Windows Name Resolution
| WINS | NETBIOS |
| Local NetBIOS Name Cache | Local Host Name |
| WINS Server | HOSTS Files |
| B-Node Broadcast | DNS |
| LMHOSTS File |
Windows Small Business Server 2003 Port Forwarding
For full functionality of SBS 2003 (SBS2003) Remote Web Workplace, forward the following ports at your router or firewall:
SMTP 25 – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
HTTP 80 – Home Page Web
SSL 443 – Home Page Web Secured
HTTP2 444 – Second SSL Secured on alternate port for SharePoint
PPTP 1723 – VPN Connections
RDP 3389 – Remote Desktop Protocol (only needed for direct access, if using RWW website, only 4125 is needed)
RWW 4125 – Remote Web Workplace
Optional:
POP3 110 – If using POP3 mail connections
IMAP 143 – Good for iPhones (1st Generation)
IMAP SSL 993 – Even better for iPhones (1st Generation)
back to top
Cisco Router Configuration Cheat Sheet
| Networking | IEEE | Cisco Term | Frame Type |
| TCP/IP | 802.3 | arpa | Ethernet II |
| Novell | |||
| Netware 3.11 or lower (default) | 802.3 | novell-ether | Ethernet 802.3 |
| Netware 3.12 or higher | 802.2 | sap | Ethernet 802.2, Token Ring, FDDI 802.2 |
| AppleTalk on TCP/IP | 802.2 | snap | Ethernet SNAP, Token Ring SNAP, FDDI SNAP |
| Address Mapping | TLA | Known | Unknown |
| Address Resolution Protocol | ARP | IP, Network, Logical, Layer 3 | MAC, Media Access Control, Hardware, Layer 2 |
| Reverse Address Resolution Protocol | RARP | MAC, Layer 2 | IP, Network, Logical, Layer 3 |
| Routing | |||
| Static Routing | ip route [dest net] [mask] [next hop address (gateway)] [admin distance] [perm] | ||
| ip route [dest net] [mask] [exit interface] [admin distance] [perm] | |||
| Distance Vector | |||
| Routing Information Protocol | RIP | ||
| Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | IGRP | ||
| Link State | |||
| Open Shortest Path First | OSPF | ||
| Hybrid (DV and LS) | |||
| Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | EIGRP | ||
| Exterior Gateway Protocols | |||
| Border Gateway Protocol | BGP | ||
| Wildcard Masks | |||
| 255.255.255.255 | any | ||
| 0.0.0.0 | host | ||
| Cisco IP Configuration Conventions | |||
| Network address of all 0s means “this network or segment” | |||
| Network address of all 1s means “all networks” | |||
| Node address of all 0s means “this node” | |||
| Node address of all 1s means “all nodes” | |||
| Entire IP address set to all 0s is the Cisco default route | |||
| Entire IP address set to all 1s is the broadcast address for all nodes on the current network | |||
TCP/IP Networking
IP Subnet Calculator http://www.subnet-calculator.com/
Subnetting guide https://www.comparitech.com/net-admin/subnetting-guide/
The IP Subnet Mask Calculator enables Subnet network calculations using network class, IP address, subnet mask, subnet bits, mask bits, maximum required IP subnets and maximum required hosts per subnet.
Basic Subnetting
| TCP IP Networking Guidelines | |||||||
| Class | Mask | Networks | Hosts Per Network | Range | |||
| A | B | C | |||||
| Full Class | A | 255.0.0.0 | 126 | 16.77 M | 1.X.X.X -126.X.X.X | ||
| B | 255.255.0.0 | 16K | 65.5 K | 128.X.X.X – 191.X.X.X | |||
| C | 255.255.255.0 | 2M | 254 | 192.X.X.X – 223.X.X.X | |||
| D | Multicasting | 224.X.X.X-239.X.X.X | |||||
| E | Scientific | 240.X.X.X-255.X.X.X | |||||
| Testing | 127.X.X.X | ||||||
| Loopback | 127.1.1.1 | ||||||
| Non-Routable Private | A | 255.0.0.0 | 1 | 16.77 M | 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 | ||
| B | 255.255.0.0 | 16 | 65.5 K | 172.16.0.0 -172.31.255.255 | |||
| APIPA | 255.255.0.0 | 16 | 65.5K | 168.294.0.0 – 168.294.255.255 | |||
| C | 255.255.255.0 | 255 | 254 | 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 | |||
| Binary | Interval | Mask | Networks | Hosts Per Network | |||
| A | B | C | |||||
| 00000000 | 254 | .0 | 1 | 16.77 M | 65.5 K | 254 | + 1 Broadcast (.255) + 1 Network Base (.0) |
| 10000000 | 128 | .128 | 0.5 | 8 M | 32 K | 124 | |
| 11000000 | 64 | .192 | 2 | 4.2 M | 16,382 | 62 | |
| 11100000 | 32 | .224 | 6 | 2.1 M | 8190 | 30 | |
| 11110000 | 16 | .240 | 14 | 1.05 M | 4094 | 14 | |
| 11111000 | 8 | .248 | 30 | 524 K | 2046 | 6 | |
| 11111100 | 4 | .252 | 62 | 262 K | 1022 | 2 | |
| 11111110 | 2 | .254 | 126 | 131 K | 510 | 0 | Invalid Class C Subnet (No Hosts) |
| 11111111 | 1 | .255 | 254 | 65.5 K | 254 | 1 | Class C Host Route (Dial-Up Networking) |
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) And Subnetting
| CIDR Suffix | # of Class C Networks | Interval | Mask | Total C Subnets | Total B Subnets | Total A Subnets | Total Hosts | |
| /32 | 1/256 | 1 | 255.255.255.255 | 1 | Class C Host Route (Dial-Up Networking) |
|||
| /31 | 1/128 | 2 | 255.255.255.254 | 126 | 32,766 | 8,388,606 | NA | Invalid Subnet |
| /30 | 1/64 | 4 | 255.255.255.252 | 62 | 16,382 | 4,194,302 | 2 | |
| /29 | 1/32 | 8 | 255.255.255.248 | 30 | 8,190 | 2,097,150 | 6 | |
| /28 | 1/16 | 16 | 255.255.255.240 | 14 | 4,094 | 1,048,574 | 14 | |
| /27 | 1/8 | 32 | 255.255.255.224 | 6 | 2,046 | 524,286 | 30 | |
| /26 | 1/4 | 64 | 255.255.255.192 | 2 | 1,022 | 262,142 | 62 | |
| /25 | 1/2 | 128 | 255.255.255.128 | NA | 510 | 131,070 | 126 | Invalid Class C Subnet |
| /24 | 1 | 1 | 255.255.255.0 | 1 | 254 | 65,534 | 254 | Full Class C |
| /23 | 2 | 2 | 255.255.254.0 | 126 | 32,766 | 510 | ||
| /22 | 4 | 4 | 255.255.252.0 | 62 | 16,382 | 1,022 | ||
| /21 | 8 | 8 | 255.255.248.0 | 30 | 8,190 | 2,046 | ||
| /20 | 16 | 16 | 255.255.240.0 | 14 | 4,094 | 4,094 | ||
| /19 | 32 | 32 | 255.255.224.0 | 6 | 2,046 | 8,190 | ||
| /18 | 64 | 64 | 255.255.192.0 | 2 | 1,022 | 16,382 | ||
| /17 | 128 | 128 | 255.255.128.0 | NA | 510 | 32,766 | Invalid Class B Subnet | |
| /16 | 256 | 1 | 255.255.0.0 | 1 | 254 | 65,534 | Full Class B | |
| /15 | 512 | 2 | 255.254.0.0 | 126 | 131,070 | |||
| /14 | 1024 | 4 | 255.252.0.0 | 62 | 262,142 | |||
| /13 | 2048 | 8 | 255.248.0.0 | 30 | 524,286 | |||
| /12 | 4096 | 16 | 255.240.0.0 | 14 | 1,048,574 | |||
| /11 | 8192 | 32 | 255.224.0.0 | 6 | 2,097,150 | |||
| /10 | 16384 | 64 | 255.192.0.0 | 2 | 4,194,302 | |||
| /9 | 32768 | 128 | 255.128.0.0 | NA | 8,388,606 | Invalid Class A Subnet | ||
| 255.0.0.0 | 1 | 16,777,214 | Full Class A | |||||
| Subnettting Considerations | ||||||||
| Total Sub-Network IDs = 1 per subnet + 1 per WAN Link | ||||||||
| Total Host IDs = 1 per host + 1 per router interface | ||||||||
| 1 Subnet Mask for entire network + 1 unique subnet ID for each physical segment + range of host IDs for each subnet | ||||||||
Well Known Ports
| The port numbers are divided into three ranges: the Well Known Ports, the Registered Ports, and the Dynamic and/or Private Ports. | ||||
| The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023. | ||||
| The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151 | ||||
| The Dynamic and/or Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535 | ||||
| Port Number | Type | Name | Description | Security Concerns |
| 1 | TCPMUX | TCP Port Service Multiplexer | ||
| 5 | RJE | Remote Job Entry | ||
| 7 | PING/TRACERT | ICMP ECHO – Packet Internet Groper and Trace Route | Block from Internet | |
| 13 | Daytime | Network Time Sync with Atomic Clock | ||
| 18 | MSP | Message Send Protocol | ||
| 20 | FTP-Data | File Transfer Protocol | Secure | |
| 21 | FTP-Control | File Transfer Protocol | Secure | |
| 22 | SSH | Secure Shell Remote Login Protocol | ||
| 23 | Telnet | Telnet | Secure | |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | Block Relay | |
| 29 | MSG ICP | |||
| 37 | TIME | Time | ||
| 42 | Nameserv | Host Name Server | ||
| 43 | Whois | WhoIs | ||
| 49 | Login | Login Host Protocol | ||
| 53 | DNS | Domain Name System | Secure | |
| 67 | BootP-Server | Outgoing DHCP | Block | |
| 68 | BootP-Client | Incoming DHCP | ||
| 69 | TFTP | TFTP – Trivial File Transfer Protocol | ||
| 70 | Gopher | Gopher | ||
| 79 | Finger | Finger | ||
| 80 | HTTP | HTTP | ||
| 88 | Kerberos | Secure Encrypted Login | ||
| 103 | X.400 | X.400 | ||
| 108 | SNA | SNA Gateway Access Server | ||
| 109 | POP2 | Post Office Protocol | ||
| 110 | POP3 | Post Office Protocol | ||
| 115 | SFTP | Simple File Transfer Protocol | ||
| 118 | SQL | SQL Services | ||
| 119 | NNTP | Network News Transfer Protocol | ||
| 135 | Both | NetBIOS | DCE Endpoint Mapper | Block |
| 137 | Both | NetBIOS | NetBIOS Name Service | Block |
| 138 | Both | NetBIOS | NetBIOS Datagram Service | Block |
| 139 | Both | NetBIOS | NetBIOS Session Service | Block |
| 143 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol | ||
| 150 | NetBIOS | NetBIOS Session Service | ||
| 156 | SQL | SQL Server | ||
| 161 | SNMP | SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol | ||
| 179 | BGP | BGP – Border Gateway Protocol | ||
| 190 | GACP | Gateway Access Control Protocol (GACP) | ||
| 194 | IRC | IRC – Internet Relay Chat | ||
| 197 | DLS | Directory Location Service (DLS) | ||
| 213 | IPX | Novell Netware | ||
| 389 | LDAP | LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol | ||
| 396 | Novell Netware over IP | |||
| 443 | HTTPS | HTTP over TLS/SSL | Enable only if required – otherwise BLOCK | |
| 444 | SNPP | Simple Network Paging Protocol (SNPP) | ||
| 445 | Microsoft-DS | Block | ||
| 458 | Apple Quick Time | |||
| 546 | DHCPv6 | DHCP version 6 Client | ||
| 547 | DHCPv6 | DHCP version 6 Server | ||
| 563 | NTTPS | Network News Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL | ||
| 569 | MSN | |||
| 636 | LDAPS | LDAP over TLS/SSL | ||
| 989 | FTPS-DATA | FTP Data over TLS/SSL | ||
| 990 | FTPS | FTP Control over TLS/SSL | ||
| 992 | TenetS | Telnet over TLS/SSL | ||
| 993 | IMAP4S | IMAP over SSL | ||
| 994 | IRCS | IRC over TLS/SSL | ||
| 995 | POP3S | Post Office Protocol 3 over TLS/SSL | ||
| Private Ports | ||||
| 1080 | Socks | |||
| 1512 | Both | WINS | Windows Internet Naming Service | |
| INSTANT MESSAGING PORTS | ||||
| 4443 | TCP | AIM | AOL | Block or Permit |
| 5190 | TCP | AIM | AOL | Block or Permit |
| 3574 | TCP | ICQ | Block or Permit | |
| 4000 | UDP | ICQ | Block or Permit | |
| 4001 | UDP | ICQ | Block or Permit | |
| 5190 | TCP | ICQ | Block or Permit | |
| 7320 | TCP | ICQ | Block or Permit | |
| 1503 | TCP | MSN | MSN Messenger | Block or Permit |
| 1863 | TCP | MSN | MSN Messenger | Block or Permit |
| 6891 | TCP | MSN | MSN Messenger | Block or Permit |
| 13324 | UDP | MSN | MSN Messenger | Block or Permit |
| 13325 | UDP | MSN | MSN Messenger | Block or Permit |
| 5010 | TCP | Yahoo | Block or Permit | |
Click this link for to be directed to a comprehensive port number list on the IANA web site.
IRQs
| IRQ | DEVICE | PORT |
| 0 | Timer | |
| 1 | Keyboard | |
| 2 | Video Adapter (maybe be redirected to 9) | |
| 3 | Serial Port COM2 or COM4 (available) | 2F8 |
| 4 | COM1 or COM3 | 3F8 |
| 5 | LPT2 (available) | 278 |
| 6 | Floppy Disk Controller | |
| 7 | LPT1 (Parallel Port) | 378 |
| 8 | Real-Time Clock | |
| 9 | Redirected IRQ2 (available) | |
| 10 | Available | |
| 11 | Available | |
| 12 | PS2 Mouse (available) | |
| 13 | Math Coprocessor | |
| 14 | Hard Disk Controller | |
| 15 | Available |
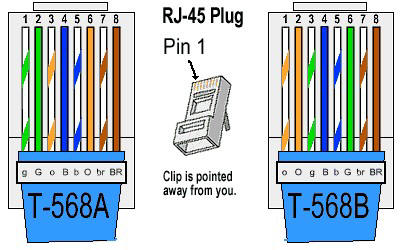
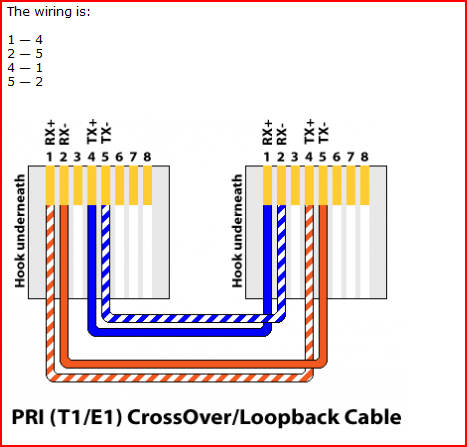
Ethernet Wiring
| Pin | Straight 568B | 568A | Cross-Over | Phone |
| 1 | Orange White | Green White | Brown | Brown White |
| 2 | Orange | Green | Brown White | Green White |
| 3 | Green White | Orange White | Green | Orange White |
| 4 | Blue | Blue | Blue White | Blue |
| 5 | Blue White | Blue White | Blue | Blue White |
| 6 | Green | Orange | Green White | Orange |
| 7 | Brown White | Brown White | Orange | Green |
| 8 | Brown | Brown | Orange White | Brown |
568A vs. 568B. Which should you use?
There are two accepted standards for 8-wire data network jacks (commonly and incorrectly called “RJ-45.”)
ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-B “Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard” lists both wiring configurations. T568B is the most prevalent for commercial installations, and was used by AT&T for the original Merlin phone systems. To help you remember, associate “B” with “Bell.”
ANSI/TIA/EIA-570-B “Residential Telecommunications Cabling Standards” recommends T568A
If the installation is residential, choose T568A unless other conditions apply (see below).
- The two inner pairs of 568A are wired the same as a two-line phone jack.
- If there is pre-existing voice/data wiring (remodel, moves, adds, changes), duplicate this wiring scheme on any new connection.
- If project specifications are available, use the specified wiring configuration.
- If components used within the project are internally wired for either T568A or T568B, use that wiring scheme. Make sure both ends of a cable are wired the same way.
25-pair cable color codes for punch-down blocks & connectors